Intel Core i5-5200U vs Core i5-6200U vs Core i5-7200U – how the most mainstream Intel chip has matured

With the Kaby Lake generation of CPUs upon us, questions start to bother a good number of users. Is it time for an upgrade? Is it worth getting the Kaby Lake-powered notebook instead of the slightly cheaper Skylake or Broadwell counterpart? The answer to your question is in this article.
You can find most of the available Core i5-7200U-powered notebooks here: http://amzn.to/2eIavXb
We recently had the chance to test the Core i5-7200U chip in the Lenovo Yoga 910 and we were delighted by the results. Quite frankly, we were expecting only marginal gains in performance but some benchmarks prove otherwise. We even saw a significant bump in the iGPU department as you can see in the benchmarks below.
But what makes the Kaby Lake generation superior to the previous Skylake and Broadwell chips – the Core i5-6200U and Core i5-5200U? At first glance, almost nothing. All three chips are built on the 14nm node and feature practically the same architecture with some small tweaks. Going from each generation to the next, we mostly see improvements in the power management and slightly higher clock speeds leading to overall better raw performance. For instance, the Core i5-5200U (Broadwell) runs at 2.2 – 2.7 GHz (2.5 GHz with two active cores) while the Core i5-6200U (Skylake) ticks at 2.3 – 2.8 GHz (2.7 GHz for two active cores). But going to Kaby Lake, the increased clocks bring the Core i5-7200U closer to the Core i7-6500U than its direct predecessor and the jump is probably due to the improved 14nm+ process, which Intel claims to be the main feature of the new generation allowing better energy-efficiency and raw power.
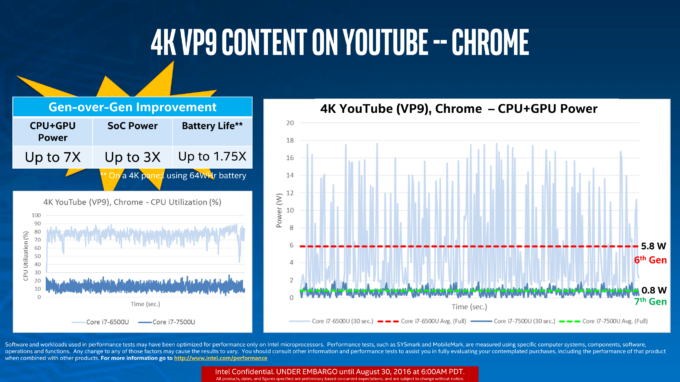
And what about iGPUs? Apparently, the Intel HD Graphics has gone a long way. The Intel HD Graphics 5500 brought a big performance over Haswell’s iGPUs but Intel has managed to perfect even more the HD Graphics 520 (Skylake) and HD Graphics 620 (Kaby Lake). Especially when it comes to power efficiency. Intel has addressed the issue by improving the already presented features in the Skylake generation and allowing for a full hardware acceleration for encoding and decoding of 4K HEVC content. This improves not only performance but the new method is superior to the older hybrid-like process in terms of power efficiency as well. Along with the HEVC encode, the Kaby Lake generation of CPUs also deliver the VP9 encoding that’s been used by Google in their YouTube videos. So to recap things, the Kaby Lake generation relies only on hardware decoding the VP 10-bit, 8-bit and HEVC Main10 codecs instead of using hybrid acceleration as seen in the Skylake and Broadwell chips.
However, the EU count hasn’t been changed (24 Execution Units), although Intel claims the higher clock speeds in the HD Graphics 520 and 620 have not affected the overall power consumption. For the record, Intel’s HD Graphics 5500 on the i5-5200U is running at 300 – 900 MHz while the HD Graphics 520 and 620 go a tad higher at 300 – 1000 MHz. We would also like to note that the direct comparison between the three graphics processors is slightly skewed due to the fact that Broadwell-powered machines didn’t support DDR4 memory, which is vital for iGPU performance. You can see how the shift to DDR4 has influenced the performance of the Intel HD Graphics 520.
Specifications
| Intel Core i5-7200U | Intel Core i5-6200U | Intel Core i5-5200U | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cores | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Threads | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Base Frequency | 2.5 GHz | 2.3 GHz | 2.2 GHz |
| Turbo Boost Frequency | 3.1 GHz | 2.8 GHz | 2.7 GHz |
| Graphics | Intel HD Graphics 620 | Intel HD Graphics 520 | Intel HD Graphics 5500 |
| GPU clock | 300 – 1000 MHz | 300 – 1000 MHz | 300 – 900 MHz |
| EUs | 24 | 24 | 24 |
| TDP | 15W | 15W | 15W |
| Cache | 3MB | 3MB | 3MB |
| DDR4 support | 2133 MHz | 2133 MHz | No |
Benchmarks
As you can see from the results below, the Core i5-7200U offers a maximum of just 14% better performance over the Core i5-6200U in multi-core benchmarks. The change might be solely due to the higher clock speeds, which is a good thing because you get better performance per watt.
CPU performance
Results are from the Cinebench 20 CPU test (the higher the score, the better)
Results are from our Photoshop benchmark test (the lower the score, the better)
Results are from the Fritz chess benchmark (the higher the score, the better)
GPU performance
Graphics performance, however, is a whole another story. Some benchmarks show as high as 25% better score compared to the HD Graphics 520 running on DDR4-2133 RAM and even bigger difference compared to notebooks using DDR3L-1600 RAM. We even think that gaming on the HD Graphics 620 is conditionally possible.
Results are from the 3DMark: Fire Strike (Graphics) benchmark (higher the score, the better)
Results are from the Unigine Superposition benchmark (higher the score, the better)
You can find most of the available Core i5-7200U-powered notebooks here: http://amzn.to/2eIavXb
Conclusion
 If you are coming from a Haswell notebook, the upgrade might be a necessity for some and the same thing can be said about Broadwell owners, although most users won’t notice the difference in day-to-day tasks like office work, browsing etc. More demanding applications, however, will run snappier and smoother on the newer generation of Skylake and Kaby Lake CPUs due to the number of under the hood tweaks and features. This also answers our next question whether it’s a good idea upgrading from Skylake to Kaby Lake. Probably not, unless…
If you are coming from a Haswell notebook, the upgrade might be a necessity for some and the same thing can be said about Broadwell owners, although most users won’t notice the difference in day-to-day tasks like office work, browsing etc. More demanding applications, however, will run snappier and smoother on the newer generation of Skylake and Kaby Lake CPUs due to the number of under the hood tweaks and features. This also answers our next question whether it’s a good idea upgrading from Skylake to Kaby Lake. Probably not, unless…
For whatever reason, you need extra GPU power. Our initial tests of the HD Graphics 620 show more than just marginal performance gains. And if you go for a DDR4-2133-equipped notebook – which is more probable nowadays as everyone is shifting to the newer standard – you will be quite satisfied with the speeds you get.
Otherwise, we suggest keeping your current Broadwell or Skylake-powered notebook for at least another year until Intel introduces its next manufacturing process. Most users won’t feel the actual difference unless battery life is involved. Unfortunately, though, we cannot confirm the latter unless we test an identical system with Core i5-6200U and Core i5-7200U and check if Intel’s claims are true.